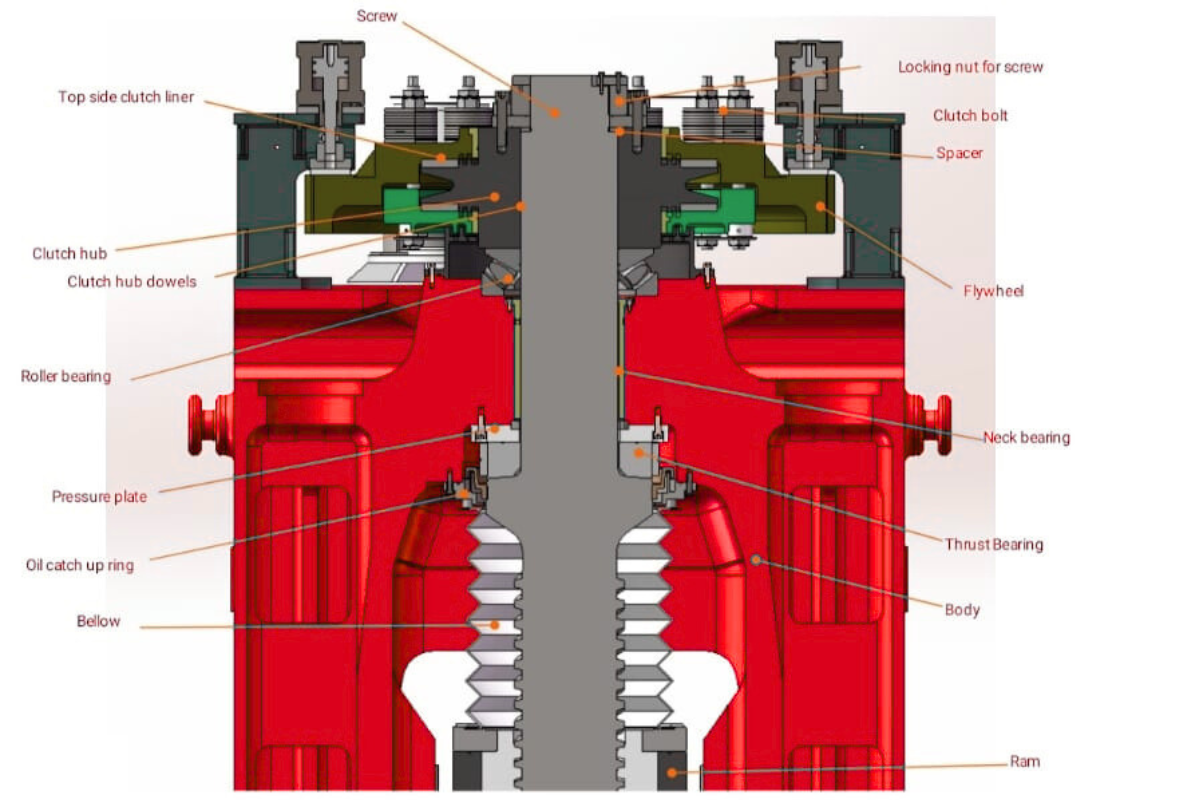
When the motor or flywheel rotates, the clutch hub engages, transmitting motion to the screw, which moves the ram downward to apply forging pressure.
After the stroke, the screw reverses, raising the ram for the next cycle. Bearings, liners, and lubrication systems ensure durability and efficiency.
🔹 1. Screw
The main vertical shaft that converts rotational motion into linear force. When the screw rotates, it moves the ram (forging slide) up or down, generating the forging stroke.
🔹 2. Locking Nut for Screw
Secures the screw in position and prevents unwanted axial movement or loosening during heavy forging loads.
🔹 3. Clutch Bolt
Connects and locks the flywheel to the screw shaft through the clutch hub, allowing torque transmission during forging strokes.
🔹 4. Spacer
Maintains the correct axial distance between components and ensures alignment within the upper assembly.
🔹 5. Flywheel
Stores rotational energy and releases it instantly during the press stroke. It helps deliver high impact energy to the forging operation efficiently.
🔹 6. Clutch Hub
Engages or disengages the flywheel with the screw. When engaged, it transfers the flywheel’s energy to the screw to move the ram.
🔹 7. Clutch Hub Dowels
Provide a rigid and precise connection between the clutch hub and the screw shaft, ensuring accurate torque transfer.
🔹 8. Top Side Clutch Liner
A frictional surface material that helps in smooth clutch engagement, minimizing wear and ensuring controlled power transmission.
🔹 9. Roller Bearing
Supports the rotational movement of the screw and flywheel assembly, reducing friction and allowing smooth operation.
🔹 10. Pressure Plate
Transmits the pressure from the clutch hub to the screw during engagement. It also helps in dissipating heat generated due to friction.
🔹 11. Oil Catch-Up Ring
Prevents oil leakage from the bearings and moving parts by collecting and redirecting lubricating oil back to the system.
🔹 12. Bellow
A flexible seal that prevents dust, scale, or foreign material from entering the screw threads while allowing vertical movement.
🔹 13. Neck Bearing
Provides support to the upper part of the screw and helps maintain alignment during rotation and impact load.
🔹 14. Thrust Bearing
Takes up the vertical thrust loads generated during forging strokes, ensuring smooth operation and protecting other components from excessive stress.
🔹 15. Body
The main structural frame of the press that supports all components and absorbs the forging forces during operation.
🔹 16. Ram
The lower moving part connected to the screw that directly applies force to the die or workpiece, performing the forging operation.